Click here to read this mailing online.
|
Penn Researchers Improve Living Tissues With 3D Printed Vascular Networks Made From SugarBioengineers can already make 2D structures out of many kinds of tissue, but one of the major roadblocks to making the jump to 3D is keeping the cells within large structures from suffocating; organs have complicated 3D blood vessel networks that are still impossible to recreate in the laboratory.
Now, University of Pennsylvania researchers have developed an innovative solution to this perfusion problem: they’ve shown that 3D printed templates of filament networks can be used to rapidly create vasculature and improve the function of engineered living tissues.

Nature Materials - Rapid casting of patterned vascular networks for perfusable engineered three-dimensional tissues Read more » Successful businesses will be those that optimize the mix of humans, robots, and algorithmsTechnology Review - In Automate This, a book due out next month, author and entrepreneur Christopher Steiner tells the story of stockbroker Thomas Peterffy, the creator of the first automated Wall Street trading system. Using a computer to execute trades, without humans entering them manually on a keyboard, was controversial in 1987—so controversial that Nasdaq pressured him to unplug from its network. Then, with a wink, Peterffy built an automated machine that could tap out the trades on a traditional keyboard—technically obeying Nasdaq rules. Peterffy made $25 million in 1987 and is now a billionaire.
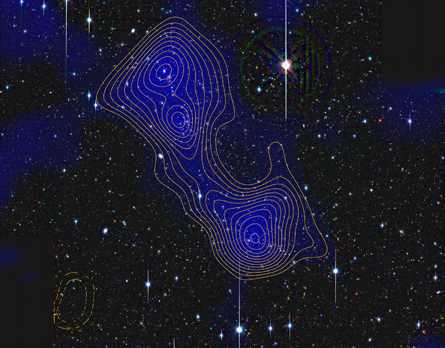
Today, automated trading bots account for nearly three-quarters of U.S. equity trading by volume. Trading houses plow millions into fiber optics and microwave dishes so their algorithms can send trades a millisecond faster than the next guys'. And although the first trading robot was built 25 years ago, most of the change on Wall Street has occurred during just the last few years. When it comes to automation, we may be in the elbow of an exponential curve. Robots made by Kiva Systems move product shelves on a warehouse floor. Amazon bought the company earlier this year in a step toward automating its distribution system and reducing labor costs. Kiva Systems Read more » Observation and Measurement of a 59 million light year long Dark Matter FilamentNature - A ‘finger’ of the Universe’s dark-matter skeleton, which ultimately dictates where galaxies form, has been observed for the first time. Researchers have directly detected a slim bridge of dark matter joining two clusters of galaxies, using a technique that could eventually help astrophysicists to understand the structure of the Universe and identify what makes up the mysterious invisible substance known as dark matter.
The presence of dark matter is usually inferred by the way its strong gravity bends light travelling from distant galaxies that lie behind it — distorting their apparent shapes as seen by telescopes on Earth. But it is difficult to observe this 'gravitational lensing' by dark matter in filaments because they contain relatively little mass. Dark-matter filaments, such as the one bridging the galaxy clusters Abell 222 and Abell 223, are predicted to contain more than half of all matter in the Universe. Jörg Dietrich, University of Michigan/University Observatory Munich Read more » More Recent Articles
|